low normal lv systolic function Systolic heart failure is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart can’t pump blood efficiently. It can be caused by various factors, such as coronary artery disease or hypertension, and can lead to fluid buildup and organ damage. Learn how to diagnose and treat this serious condition. See more Toxic Blowpipe: This is a powerful Ranged weapon that has one of the best attack speeds in OSRS. The powerful special attack will deal more damage and heal you. It requires level 75 Ranged to wield and can be made from a Tanzanite Fang with level 53 Fletching. Attack Bonuses: +30 Ranged; Other Bonuses: +20 Ranged Strength
0 · what causes low ejection fraction
1 · treatment for low ejection fraction
2 · systolic heart failure concept map
3 · reduced ejection fraction symptoms
4 · lv systolic function severely reduced
5 · end stage systolic heart failure
6 · ejection fraction chart
7 · ejection fraction 55 60
DOT 4 LV can be used in all vehicles that require DOT 4 fluid. Kinematic Viscosity at 40°C 6.4 mm2/s. DESCRIPTION. Pentosin DOT 4 LV is a special brake fluid of highest DOT 4 performance levels and extremely low viscosity at cold temperatures.
Systolic heart failure is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart can’t pump blood efficiently. It can be caused by various factors, such as coronary artery disease or hypertension, and can lead to fluid buildup and organ damage. Learn how to diagnose and treat this serious condition. See moreSystolic heart failure is a condition in which the left ventricle of your heart is weak. Your left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber of your heart. It’s . See moreSystolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(HFrEF). Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage . See more
Anyone can develop systolic heart failure, but it’s more common as people age. It typically occurs in people who have had another heart-related condition. See more
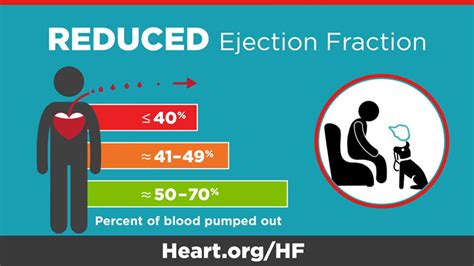
Ejection fraction (EF) is a percentage of blood pumped out by the left ventricle with each contraction. A normal EF is 55-70 percent, but a low EF can indicate heart failure or . A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart. Reduced left ventricular systolic function predicts worse outcomes. However, the optimal threshold for “normal” left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is uncertain. In general .
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV .Ejection fraction measures your heart’s ability to pump oxygen-rich blood out to your body. In a healthy heart, the fraction is a higher number. A low number means that your heart has .European Society of Cardiology and American Society of Echocardiography guidelines report normal LVEF as >50% and >55%, respectively (2, 3) and clinical HF trials have defined left .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are .
The clinical syndrome of heart failure (HF) can develop in patients with low, mildly decreased, or normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
what causes low ejection fraction

Learn how to assess LV systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain, and how to interpret the results in different clinical scenarios. Find out the . Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) . Normal Ejection Fraction. . With an EF of 25% or lower, your heart function is considered seriously impaired. .
chanel stroller
Normal LV systolic function.. *CONCLUSIONS: 1. small reversible myocardial perfusion defect noted in the basal anterior wall (area of reversible ischemia 3%). Low risk stress test. 2. EF 88% 3. Normal LV .Known Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. If no established diagnosis of heart failure, please see referral for suspected diagnosis of heart failure page. For patients with an established diagnosis of heart failure: Classify severity according to NYHA score. 55 to 70% – Normal heart function. 40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure.
Acute Systolic Heart Failure Versus Chronic Systolic Heart Failure. Systolic heart failure can be classified as acute or chronic: Acute: You have active symptoms of heart failure with a new diagnosis or a long-term condition. Chronic: You have a history of heart failure, but are relatively stable. Acute systolic heart failure is a medical .Complete review on left ventricular systolic function, with emphasis on echocardiography, definitions, methods and guidelines. . it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities. Fractional . This is achieved by filtering out signals with low amplitude and high velocity; such signals . In systolic heart failure, the left ventricle becomes weak and can't contract and work the way it should. . heart muscle is damaged, your heart can't pump blood as normal. Watch a video to see .
treatment for low ejection fraction
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been a key variable for the diagnosis and management of heart failure over the last three decades. The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for assessment of cardiac dimensions and function.1 They describe four categories of left ventricular function and a ‘normal’ LVEF is . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 1 has persisted as the primary measure of left ventricular systolic function despite flaws in this approach. Patients with heart failure are relieved when the LVEF is reported as normal, and clinicians may use the report of a depressed LVEF to persuade patients of the need for treatment.
Clinically, a borderline LVEF may be referred to as “low-normal.” However, our results suggest that this term for an LVEF of 50% to 55% may be misleading, and it may not convey the increased adverse risks associated with borderline LV systolic function. Moderately below normal (30% to 40%): Patients experience heart failure with reduced left ventricular function symptoms. “The heart can’t supply the demands of the body because it can’t .
Objective To investigate whether low-normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is associated with adverse outcomes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and evaluate the incremental value of predictive power of LVEF in the conventional HCM sudden cardiac death (SCD)-risk model. Methods This retrospective study included 1858 patients with HCM from .
What Is a Normal Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction? Paul Heidenreich , MD, MS L eft ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)1 has per-sisted as the primary measure of left ventricular systolic function despite flaws in this approach. Patients with heart failure are relieved when the LVEF is . percentages in the low 60s. 3 Thus, whereas LVEF per- With respect to the lower limit of “normal” LVEF, it is important to remember that even at rest, the LV pumps a slightly different amount of blood in every beat. Things like time of day (biological cycles), eating (what and when), position (supine vs. upright), breathing, medications, etc. can all slightly change LVEF in a normal person.
Among patients with primary mitral regurgitation, ejection of blood into the low-pressure left atrium can mask LV systolic dysfunction despite a normal LVEF. Contractile reserve on exercise and LV GLS might allow for earlier detection of early stage but clinically significant LV systolic dysfunction. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the .
Grading of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with preserved systolic function by the 2016 American Society of Echocardiography/European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging Recommendations .
systolic heart failure concept map

Echocardiography. Matthew TH. Lowry, Patrick H. Gibson, in Medicine, 2022. LV systolic function. Systolic function describes overall myocardial contractility, most commonly performed by assessing the change in chamber size from end-diastole to end-systole. Visual assessment of different regions of the myocardium can reveal normal, hypokinetic, akinetic or dyskinetic . fractional shortening: percentage change in LV internal dimensions between systole and diastole (normal 30-45%) preload: end-diastolic volume (if low think -> hypovolaemia, low SVR, severe AR or MR, VSD) afterload: end-systolic wall stress (rarely used in clinical practice) LV wall thickness: > 1.5cm = LVH, < 0.6cm = LV thinning; Regional Function

Congestive heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction; Left heart failure; Clinical Information. Failure of adequate output by the left ventricle despite an increase in distending pressure and in end-diastolic volume, with dyspnea, orthopnea, and other signs and symptoms of pulmonary congestion and edema. Research to Practice: Assessment of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain for Surveillance of Cancer Chemotherapeutic-Related Cardiac Dysfunction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2018;11:1196-1201. Echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) has been recommended as a means to follow patients at risk of cancer chemotherapy-related left .
Longitudinal echocardiographic data from the Framingham Heart Study demonstrate that aging is associated with increases in LV wall thickness, decreases in LV cavity size, and increases in chamber-level measures of LV systolic function (LVEF and fractional shortening). 3 Furthermore, traditional HF risk factors modify these normal age-related .
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. . with normal LV systolic function (12-year sur-vival, 73%) . showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium. Introduction. Ejection fraction (EF) is defined as the stroke volume indexed to the end-diastolic volume (EDV) and was described in the 1960s by Folse and Braunwald 1 using a radioisotope dilution technique. It has become a cornerstone of contemporary clinical practice, guiding the use of therapies and interventions across a spectrum of cardiovascular conditions.Echocardiography is the principal modality for investigating left ventricular systolic function and diastolic function. M-mode, 2D echocardiography and Doppler are all used to examine various parameters. Three-dimensional (3D) echocardiography has become increasingly common, and may be as precise as cardiac MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) for .
devil wears prada rating
Preserved left ventricular systolic function with ejection rate of 55-60%. Also trace regurgitation in mitral valve and tricuspid valve. I wont be hearing from the doctor until monday or tuesday and i am trying to figure out what those results mean? Summary of my resent echogram; 1-Low normal left ventricular function. The estimation of left ventricular systolic function, both qualitative and quantitative, is central to the management of the cardiovascular status of the surgical or critically ill patient. . For example, a fractional shortening of 30%, while “appearing” as a low percentage, actually represents normal systolic function . However, most .
sell my prada bag
Shop Motorcraft® dot 4 LV high performance motor vehicle brake fluids for Ford & Lincoln vehicles online. Search products, find where to buy, view warranty details & more.
low normal lv systolic function|end stage systolic heart failure